
Typical simulations are run on servers or workstation machines because they are more powerful. Postprocessing is done on the CPU after the solution is obtained, where the user further process the standard results to get something more meaningful. Processing is done using either the CPU or the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), solving the underlying Maxwell’s Equations to give us the solution. This part is done using the Central Processing Unit (CPU).

Preprocessing is to set up the problem, including discretizing the simulation domain and defining the excitations and boundary conditions.
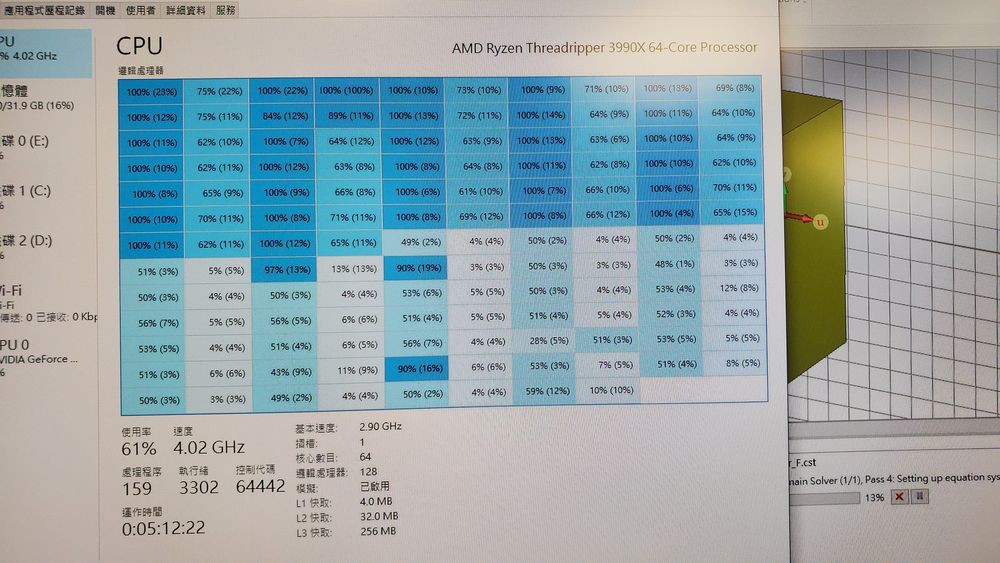
Before we delve into the focus of our post, it is relevant to explain that electromagnetic simulation processing can be broken into three parts: preprocessing, processing (solver run), and postprocessing.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
